
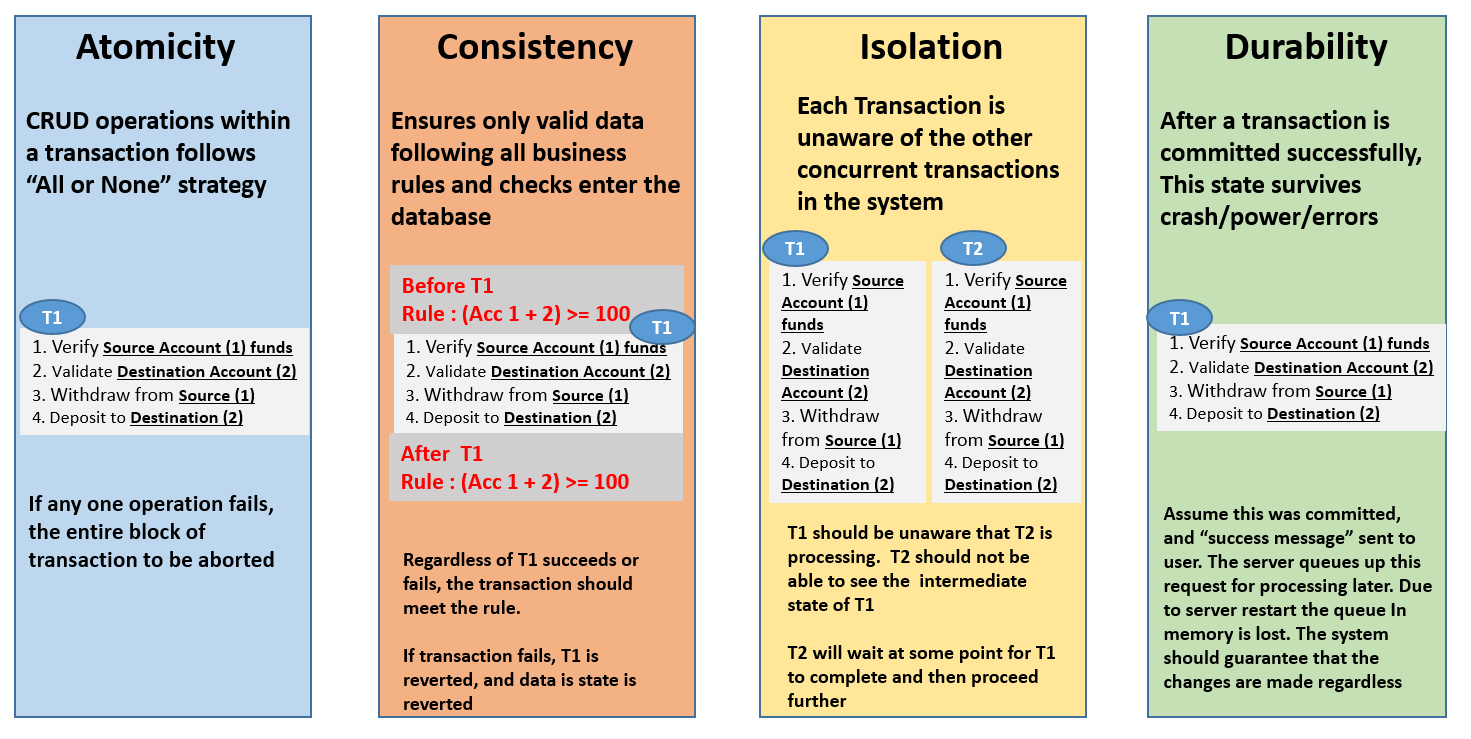
So then how do companies store and manage data? How do they ensure that the data they rely on is well. The more accurate and reliable data you have, the better your business will be at making key decisions. However, some vendors, such as MarkLogic, OrientDB, and Neo4j offer ACID compliant NoSQL database management systems.Data has become the lifeblood of modern businesses - data on sales, data on customers, data on competitors, and data on partners are all critical to leverage. Most NoSQL DBMS work on a eventually consistent basis, meaning that, data may be out of sync for a time, but it will eventually be in sync. However, most NoSQL DBMSs can provide atomicity to some degree. NoSQL databases are often designed to ensure high availability across a cluster, which usually means that consistency and/or durability is sacrificed to some degree. They all include features that ensure that the data maintains consistent throughout software and hardware crashes, as well as any failed transactions. ACID ComplianceĪll of the major relational DBMSs adhere to the ACID principles. Media failure is usually quite rare when compared to the other two types of failure. This could be caused by the media itself, or it could be due to bugs in the operating system. Media failure refers to the condition of not being able to read from or write to a storage device (such as the hard disc). System FailureĪ system failure can be caused by a bug in the DBMS code, an operating system fault, or a hardware failure. It could also be due to a timeout or deadlock in the DBMS. Types of Failure Transaction FailureĪ transaction failure could occur due to bad input or some other violation of consistency. So ACID-compliant DBMSs provide organisations with the confidence that their database will maintain data integrity, even if some type of failure occurs while transactions are in the middle of being processed. If a failure occurs before a transaction completes, no data will be changed.

Any database that is ACID-compliant will ensure that only successful transactions are processed. This is where the ACID principles should apply.Īccording to the ACID definition, a database is consistent if and only if it contains the results of successful transactions. Money could be debited from the first account but not credited to the other account. If a transaction like this fails halfway through, it could have major consequences. debiting one account and crediting the other) is a transaction. For example, transferring money between bank accounts (i.e. So ACID provides the principles that database transactions should adhere to, to ensure that data doesn’t become corrupt as a result of a failure of some sort.Ī transaction is a single logical operation that may consist of one or many steps. The ACID properties are designed as principles of transaction-oriented database recovery. Any changes from the transaction must be stored permanently. If the system tells the user that the transaction has succeeded, the transaction must have, in fact, succeeded.

Durabilityĭurability means that, once a transaction is committed, it will remain in the system – even if there’s a system crash immediately following the transaction. So a transaction cannot read data from any other transaction that has not yet completed. No transaction will be affected by any other transaction. Guarantees that all transactions will occur in isolation.
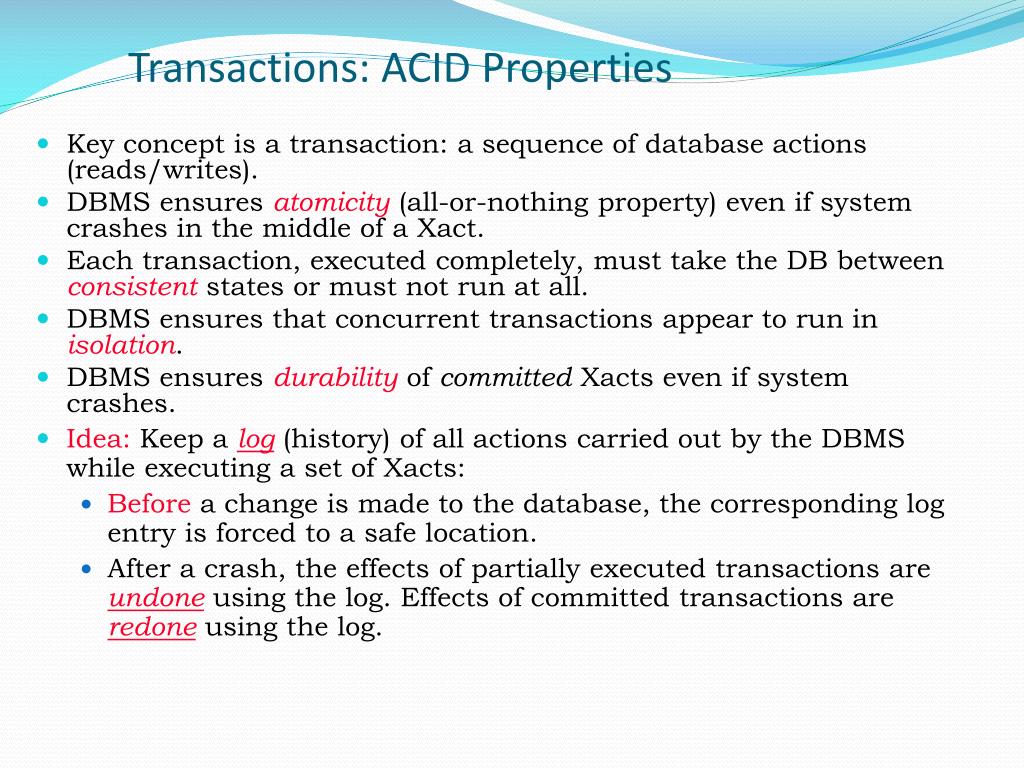
All data will be valid according to all defined rules, including any constraints, cascades, and triggers that have been applied on the database. This ensures that you guarantee that all data will be consistent. With atomicity, it’s either “all or nothing”. If one part of the transaction fails, the whole transaction fails. AtomicityĪtomicity means that you guarantee that either all of the transaction succeeds or none of it does. You don’t get part of it succeeding and part of it not.
In database systems, ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) refers to a standard set of properties that guarantee database transactions are processed reliably.ĪCID is especially concerned with how a database recovers from any failure that might occur while processing a transaction.Īn ACID-compliant DBMS ensures that the data in the database remains accurate and consistent despite any such failures.ĪCID is an acronym that stands for Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability. These are explained below.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
